VigRX Plus
General Information about VigRX Plus
Furthermore, VigRX Plus additionally incorporates Catuaba Bark Extract, a standard Brazilian aphrodisiac that has been used for generations to improve sexual performance and improve sexual need. This mixture of natural ingredients works synergistically to promote male sexual well being and improve general sexual satisfaction.
It is necessary to note, nevertheless, that VigRX Plus just isn't a magic tablet that can immediately increase penis measurement in a single day. It is designed to work steadily, with noticeable outcomes inside 2-3 months of regular use. Additionally, outcomes might differ from individual to individual, relying on elements similar to age, general health, and life-style habits.
These components work together to extend blood flow to the penis, creating more durable and longer-lasting erections. This not solely enhances sexual pleasure for men but additionally boosts confidence and self-esteem.
But does VigRX Plus really work? The quick reply is sure. The supplement has been clinically examined and confirmed to be effective in bettering male sexual operate. In one research, participants who took VigRX Plus reported a major enchancment of their erectile perform and sexual satisfaction in comparability with the placebo group.
The major ingredient in VigRX Plus is Bioperine, a spinoff of black pepper extract, which is understood for its capability to reinforce the physique's absorption of vitamins. This makes the other ingredients in the complement stronger and effective, including Asian red ginseng, saw palmetto, and hawthorn berry, all of which have been used for tons of of years in traditional medicine to improve male sexual operate.
Moreover, VigRX Plus is backed by a 67-day money-back assure, which shows the manufacturer's confidence in the product. This allows clients to try the supplement risk-free and see the results for themselves.
One of the vital thing claims of VigRX Plus is its capacity to stimulate the natural development of cells within the cavernous body of the penis, resulting in a rise in dimension. This is achieved through a unique mix of elements which have been fastidiously chosen and examined for their effectiveness in promoting male sexual well being.
In conclusion, VigRX Plus is a protected and efficient supplement for males trying to enhance their sexual well being and performance. Its distinctive blend of pure ingredients has been proven to stimulate the expansion of cells in the penis, resulting in an increase in dimension and general sexual satisfaction. With its impressive observe document and money-back assure, it is no marvel that VigRX Plus has turn out to be one of the main male enhancement supplements in the market at present.
But what units VigRX Plus apart from different male enhancement supplements is its use of a special ingredient called Epimedium Leaf Extract, also recognized as Horny Goat Weed. This pure herb has been used in Chinese drugs for tons of of years to increase libido and deal with erectile dysfunction. Studies have shown that it can enhance the production of nitric oxide, which is important for achieving and sustaining an erection.
VigRX Plus is a well-liked male enhancement supplement that has gained vital consideration and praise in recent times. Unlike different products out there, this complement has been formulated with all-natural elements that work together to supply men with a secure and efficient resolution for his or her sexual well being.
Ketotifen reportedly has been effective in relieving pruritus and wheal formation in cutaneous mastocytosis medicine cabinets surface mount order 60 caps vigrx plus amex. Recommended approaches for the treatment of osteoporosis include calcium supplementation, consideration of estrogen replacement in postmenopausal women, and use of bisphosphonates. Imatinib mesylate (Gleevec; Novartis, Basel, Switzerland) currently is the only such drug available. Mast cells bearing a codon 816 mutation isolated from marrow of patients with mastocytosis were fairly resistant to the drug. It is possible that these studies are identifying patients with a progressive clonal mast cell disorder that may one day meet the diagnostic criteria for systemic mastocytosis. Followup at yearly intervals is Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory agents have been useful in some patients whose primary manifestations are recurrent episodes of flushing, syncope, or both. Patients with a history of aspirin sensitivity should not be placed on this therapy unless they first undergo desensitization. Patients may experience a decrease in the intensity of lesions after exposure to natural sunlight. Repeated or extensive application of glucocorticoids may result in cutaneous atrophy or adrenocortical suppression. In adults, oral prednisone (40 to 60 mg/day) usually results in decreased symptoms over a 2- to 3-week period. After initial improvement, steroids usually can be tapered to an alternate-day regimen. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Glucocorticoids; Methoxypsoralen Interferon- Cladribine Patients with more advanced categories of systemic mastocytosis may be candidates for approaches directed at reducing the mast cell burden. Resolutions of ascites and increased bone remineralization also have been reported. Its use is not routinely recommended for patients with indolent systemic disease, unless there is concomitant severe osteoporosis. Cladribine (2-chlorodeoxyadenosine), a nucleoside analogue, does not require cells in active cell cycle to exert its cytotoxic activity and may be beneficial in slowly progressing neoplastic processes. The drug has myelosuppressive and immunosuppressive properties and thus cannot be recommended for patients with indolent disease. Mast Cell Sarcoma Mast Cell Activation Syndrome this is an exceedingly rare tumor, characterized by nodules at various cutaneous and mucosal sites. Diagnostic criteria have been proposed to separate this proposed entity from other causes of such clinical findings. These criteria include response to antimediator therapy and an elevation in a marker of mast cell activation, such as serum tryptase, with an episode. Patients must be followed regularly in the event that one of the diagnoses eliminated during the initial evaluation reaches the level of diagnosis. Murakami M, Izumi H, Morimoto S, et al: Thalassemia intermedia complicated by hemochromatosis: Clinical and autopsy report of a case. Ducrest S, Meier F, Tschopp C, et al: Flow cytometric analysis of basophil counts in human blood and inaccuracy of hematology analyzers. Ishizaka T, Iwata M, Ishizaka K: Release of histamine and arachidonate from mouse mast cells induced by glycosylation-enhancing factor and bradykinin. Ganser A, Lindemann A, Seipelt G, et al: Effects of recombinant human interleukin-3 in aplastic anemia. Kitamura Y: Heterogeneity of mast cells and phenotypic change between subpopulations. Evidence that signaling through the c-kit receptor can induce expression of cellular function. Splenectomy Splenectomy has been performed on patients with severe aggressive mastocytosis in an attempt to improve their limiting cytopenias. Patients who had undergone splenectomy appeared to be better able to tolerate chemotherapy. Few of these patients progress to more severe forms of the disease; some patients may even experience a diminution in the severity of skin lesions in later years, while their marrow findings remain unchanged. Peptic ulcer and gastrointestinal bleeding, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, and lymph node enlargement are frequent findings. The total leukocyte count varies from 10,000 to 150,000/L (10 to 150 × 109/L), and mast cells compose 10 to 90 percent of leukocytes. Marrow biopsy shows a striking increase in mast cells, sometimes up to 90 percent of marrow cells, although the leukemic mast cells often are hypogranular or agranular. Siegmund R, Vogelsang H, Machnik A, et al: Surface membrane antigen alteration on blood basophils in patients with Hymenoptera venom allergy under immunotherapy. Oh C, Suzuki S, Nakashima I, et al: Histamine synthesis by non-mast cells through mitogen-dependent induction of histidine decarboxylase. Xu X, Zhang D, Zhang H, et al: Neutrophil histamine contributes to inflammation in mycoplasma pneumonia. Their value for the analysis of the roles of mast cells in biologic responses in vivo. Karasuyama H, Mukai K, Obata K, et al: Nonredundant roles of basophils in immunity. Koshino T, Teshima S, Fukushima N, et al: Identification of basophils by immunohistochemistry in the airways of post-mortem cases of fatal asthma. Partial inhibition of the reaction with antiserum against tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
The latter two cytokines are available as recombinant pharmaceutical products that can be administered therapeutically to ameliorate certain causes of neutropenia medicine januvia discount generic vigrx plus canada. Neutrophil interaction with endothelium is mediated by selectins, glycoproteins with sugar-binding sites that support shear-dependent rolling on endothelium, and by integrins on the neutrophil binding to ligands on the endothelial cells, permitting firm attachment to endothelium and emigration into tissues. Neutrophils have a short life span in blood, with a disappearance halftime of approximately 7 hours. The process can be accelerated when inflammation is present and highlights the need for a sustained rate of production to maintain a normal blood neutrophil count. The pathogenesis of neutropenia is more complex to analyze kinetically than anemia or thrombocytopenia because at least four compartments are involved: marrow storage pool, circulating pool, marginated pool, and tissue pool. Measurements can be further complicated in the nonsteady state, when dramatic increases in turnover rates and distribution among the four principal pools are in disequilibrium, as occurs during acute inflammatory states. These cytokines regulate the production, survival, and functional activity of neutrophils. Neutrophil production and neutrophil kinetics usually are analyzed by describing neutrophil movement through a number of interconnected compartments. The complexities of analyzing these compartments are covered in several recent reviews. Myeloblasts, promyelocytes, and myelocytes are capable of replication and constitute the mitotic compartment. Earlier progenitor cells are few in number, not morphologically identifiable, and usually neglected in kinetic studies. Metamyelocytes, bands, and mature neutrophils, none of which replicate, constitute the maturation storage compartment. The average number of cell divisions from the myeloblast to the myelocyte stage in the proliferative compartment has been estimated between four and five. The major increase in neutrophil number probably occurs at the myelocyte level, because the myelocyte pool is at least four times the size of the promyelocyte pool. Because of the difficulties in measuring human intramarrow neutrophil kinetics, a precise model of the dynamics of the mitotic compartment is not available. Table 611 lists the estimated sizes of the marrow neutrophil compartments and the transit times and cell-cycle stages of the cells in the various compartments. Myeloblasts undergo division and maturation into promyelocytes and thereafter into neutrophilic myelocytes after which stage mitotic capability is lost. The major compartments of precursor proliferation and distribution are indicated across the top of the figure: marrow, blood, and tissues. Under normal conditions, cells do not return from the tissue compartment to the blood or marrow. Marrow Neutrophil Kinetics Fraction in Mitosis (Mitotic Index) Mitotic compartment Myeloblast Promyelocyte Myelocyte Maturation storage compartment Metamyelocyte Band Polymorphonuclear neutrophil 8108 1296 0120 2. Radioautographic studies with [3H]thymidine support the concept of an orderly progression from metamyelocytes to mature neutrophils within the maturation storage compartment. These studies also suggest a "first in, first out" pattern for cells leaving this compartment and entering the blood. Several labeling techniques indicate the myelocyte-to-blood transit time is 5 to 7 days. Studies in dogs suggest some immature neutrophils die in the marrow ("ineffective granulopoiesis"). At present, however, no convenient means of quantitating ineffective granulopoiesis is available. On completion of maturation, the neutrophils are stored in the marrow and are referred to as the mature neutrophil reserve. Table 612 lists comparative data on the characteristics of the maturation storage compartment. Under stress, maturation time may be shortened, divisions may be skipped, and release into the blood may occur prematurely. The Blood Neutrophils leave the marrow storage compartment and enter the blood without significant reentry into the marrow. Some of these neutrophils are free in the circulation (the circulating pool), while others roll along the endothelium of small vessels or are temporarily sequestered in the alveolar capillaries of the lung (the marginated pool). Thus, neutrophils newly released from the marrow are as likely to leave the blood as are neutrophils that have been circulating for several hours. Neutrophils also are eliminated by programmed cell death and disposed of by the macrophage system. Although the observation has been clearly confirmed by numerous laboratories in different species of animals, the extent to which this phenomenon contributes to the marginated pool of neutrophils is uncertain. A more compelling concept of the marginated pool is derived from investigations of the vascular bed of the lung. A distinctive characteristic of this tissue is the complex interconnecting network of short capillary segments where the path from arteriole to venule crosses several alveolar walls (often more than eight) and often contains more than 50 capillary segments. Comparative Data on Marrow Maturation Storage Compartment Size (Cells × 109 kg) 6. The increased transit time results primarily from the time neutrophils are stopped within this vascular network. The longer time required for the neutrophils to pass through this bed apparently accounts for their increased concentration. Recruitment of neutrophils into the lungs through the alveolar capillary network contrasts with the recruitment of neutrophils through postcapillary venules at sites of inflammation in a number of important ways. The tethering mechanisms required to capture neutrophils from flowing blood in larger vessels apparently are not necessary in the alveolar capillary bed. The diameters of spherical neutrophils (6 to 8 µm) are larger than the diameters of many capillary segments (2 to 15 µm).
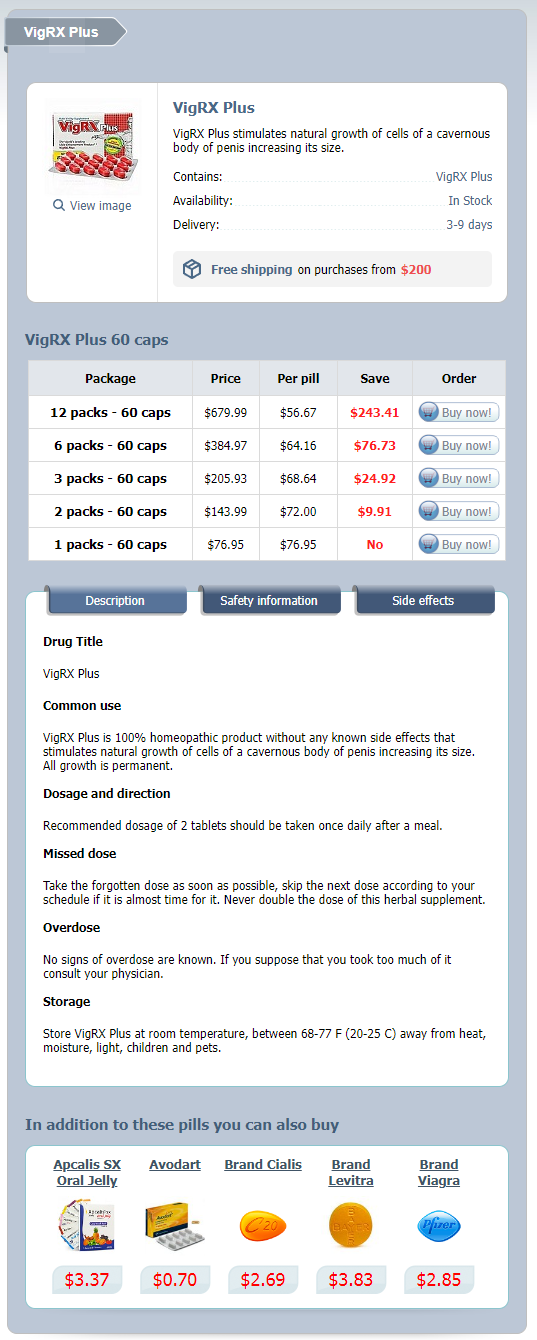
VigRX Plus Dosage and Price
VigRX Plus 60 caps
- 12 packs - $679.99
- 6 packs - $384.97
- 3 packs - $205.93
- 2 packs - $143.99
- 1 packs - $76.95
Pui C-H medications 126 cheap 60caps vigrx plus mastercard, Stass S, Green A: Bone marrow necrosis in children with malignant disease. Liang R: How I treat and monitor viral hepatitis B infection in patients receiving intensive immunosuppressive therapies or undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bürger B, Zimmermann M, Mann G, et al: Diagnostic cerebrospinal fluid examination in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Significance of low leukocyte counts with blasts or traumatic lumbar puncture. Ito C, Kumagai M, Manabe A, et al: Hyperdiploid acute lymphoblastic leukemia with 51 to 65 chromosomes: A distinct biological entity with a marked propensity to undergo apoptosis. Schrappe M: Minimal residual disease: Optimal methods, timing, and clinical relevance for an individual patient. Gaipa G, Basso G, Biondi A, Campana D: Detection of minimal residual disease in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Kager L, Cheok M, Yang W, et al: Folate pathway gene expression differs in subtypes of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and influences methotrexate pharmacodynamics. Stock W, La M, Sanford B, et al: What determines the outcomes for adolescents and young adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia treated on cooperative group protocols Toyoda Y, Manabe A, Tsuchida M, et al: Six months of maintenance chemotherapy after intensified treatment for acute lymphoblastic leukemia of childhood. Sather H, Miller D, Nesbit M, et al: Differences in prognosis for boys and girls with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Schmiegelow K, Glomstein A, Kristinsson J, et al: Impact of morning versus evening schedule for oral methotrexate and 6-mercaptopurine on relapse risk for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Manera R, Ramirez I, Mullins J, Pinkel D: Pilot studies of species-specific chemotherapy of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia using genotype and immunophenotype. Associazione Italiana Ematalogia Oncologia Pediatrica and the Berlin-Frankfurt-Munster groups. Tucunduva L, Ruggeri A, Sanz G, et al: Risk factors for outcomes after unrelated cord blood transplantation for adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A report on behalf of Eurocord and the Acute Leukemia Working party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Mohty M, Labopin M, Volin L, et al: Reduced-intensity versus conventional myeloablative conditioning allogeneic stem cell transplantation for patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A retrospective study from the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Campana D, Leung W: Clinical significance of minimal residual disease in patients with acute leukaemia undergoing haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Paganin M, Zecca M, Fabbri G, et al: Minimal residual disease is an important predictive factor of outcome in children with relapsed "high-risk" acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Doney K, Hagglund H, Leisenring W, et al: Predictive factors for outcome of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Borgmann A, Schmid H, Hartmann R, et al: Autologous bone-marrow transplants compared with chemotherapy for children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in a second remission: A matched-pair analysis. Borgmann A, von Stackelberg A, Hartmann R, et al: Unrelated donor stem cell transplantation compared with chemotherapy for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in a second remission: A matched-pair analysis. Spyridonidis A, Labopin M, Schmid C, et al: Outcomes and prognostic factors of adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia who relapse after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Association of the Nordic Cancer Registries and the Nordic Society of Paediatric Haematology and Oncology. Gokbuget N, Stanze D, Beck J, et al: Outcome of relapsed adult lymphoblastic leukemia depends on response to salvage chemotherapy, prognostic factors, and performance of stem cell transplantation. Subsequent studies revealed the involvement of the spleen and marrow and led to the introduction of the term "lymphosarcoma. This cancer is more common in men,2 uncommon in patients younger than the age of 40 years, and extremely rare in children. The risk also increases progressively with age3 and decreases with increasing parity in women. In the last few years there has been a tremendous growth in the understanding of the disease biology, which has resulted in the development of numerous new therapeutic options with resultant transformation in the management of this illness. Despite the significant improvement in the prognosis of this disease, cure currently remains elusive. The progressive accumulation of leukemic B cells is a consequence of defective apoptosis and survival signals derived from the microenvironment. Progressive disease results in dysregulation of the cellular and humoral components of the effector immune system with a resultant increase in the incidence of infectious complications, which constitutes the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in this disease. Significant therapeutic advances have been realized in recent years, especially with the development of welltolerated targeted antibodies and kinase inhibitors. Although not curative, these therapies have resulted in significant improvements in patient outcomes with substantial increases in progression-free and overall survival intervals. Multiple novel agents are also in development with the potential to alter the treatment paradigms for this disease and ultimately to affect a cure. Factors that were found to be protective include a history of allergies, blood transfusions, sun exposure, and smoking. Their survival can be extended when these cells are cultured on stromal cells or nurse like cells that are generally found in the secondary lymphoid organs. Other abnormalities that were identified in significant numbers include del 6q21 and del 17p13. With regards to other cytogenetic abnormalities, trisomy 12 is often found in patients with progressive or relapsed disease or Richter transformation. A vast majority of patients may not have any significant symptoms related to the disease but some patients may experience mild fatigue or minor limitations in their activities of daily living. A subset of patients may present with recurring infectious complications, especially upper respiratory tract infections.